Understanding the Role of Meta Tags: A Beginners Guide

Meta tags are an essential part of SEO because they provide information to search engines and users about the content of a web page.
The meta title tag appears as the clickable headline in search engine results, influencing click-through rates and attracting potential visitors.
On the other hand, meta description tags summarize the page’s content below the title tag.
By optimizing meta tags with relevant keywords,compelling descriptions, and accurate representations of the page content,
website owners can improve their chances of ranking higher in search engine results and increase the likelihood of users clicking on their pages.
Meta tags play a crucial role in on-page optimization by providing information about a web page’s content to search engines.
They are HTML tags inserted into the head section of a webpage’s code.
What Are Meta tags?
Meta tags are HTML tags that provide metadata or additional information about a web page.
It is placed within the <head> section of an HTML document and is not visible to website visitors when they view the page in a web browser.
Meta tags serve various purposes, including informing search engines and other web services about the content of a web page.

Some common types of meta tags are as follows:
- Title Tag
- Meta Description Tag
- Canonical Tag
- Alternative Text Tag
- Robots Meta Tag
- Open Graph Meta Tag
- Header Tag
What is the Title tag?
The title tag is an HTML element that appears in the header section of a web page and provides a brief and accurate description of the content on the page.
The title of a web page appears at the top of a web browser’s window and is also displayed in search engine results as the clickable headline for each search result.
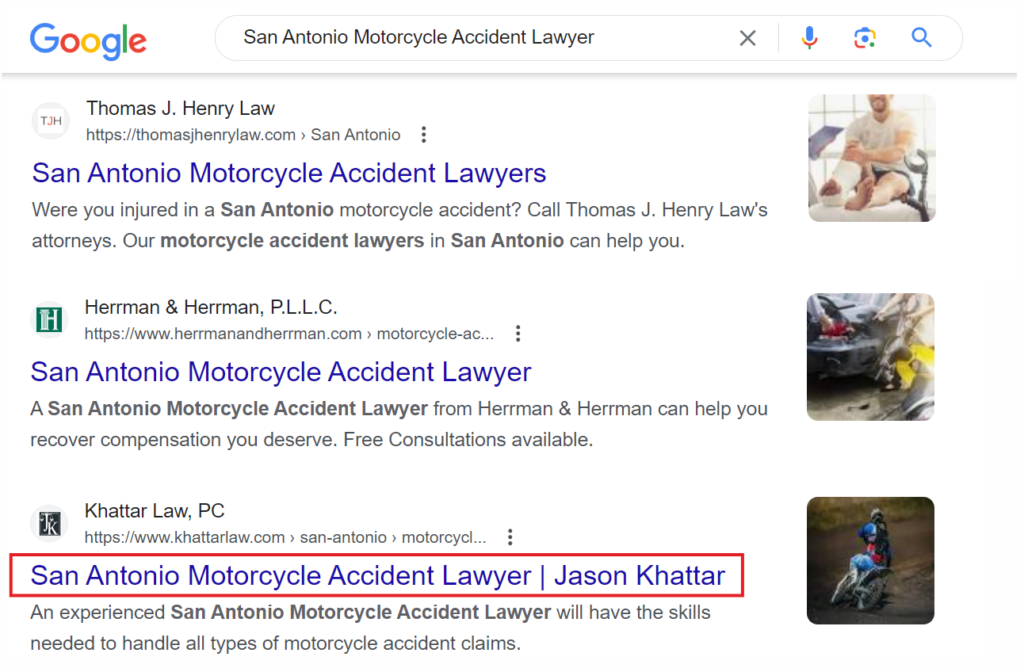
When writing a title tag for a website, there are a few key things to keep in mind to make it effective:
- Your title should be short and to the point, ideally no more than 60-65 characters. This ensures that it will display properly in search engine results and won’t get cut off.
- Include keywords that accurately reflect the content of your website and that users are likely to search for.
- If your website is associated with a specific brand, include the brand name in the title to help build brand recognition.
- Ensure that each page on your website has a unique title that accurately reflects the content of that page.
- Use vertical bars (|) or dashes (-) to separate different elements of your title, such as the brand name and keywords.
- To write a title tag for a web page, summarize the main topic or purpose of the page using relevant keywords and ensure it accurately represents the content of the page.
- When writing a title tag for a web blog, capture the essence of the blog post in a concise and attention-grabbing sentence, incorporating relevant keywords to optimize search engine visibility.
What is a Meta Description Tag?
A meta description Tag is an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary or description of the content on a web page.
It appears below the title of a page in search engine results and is designed to provide potential visitors with a quick overview of what the page is about.
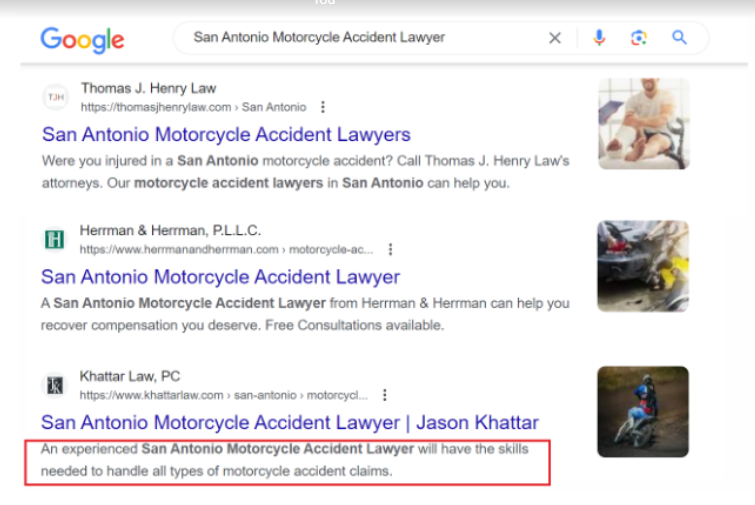
Importance of meta description
A meta description tag gives users a brief explanation of what a particular website is about, educating and engaging them,
They operate as a sales pitch, persuading the user that the page contains all the information they need.
Key aspects of the role of a meta description are as follows:
- Search Engine Results: Search engines often display the meta description as a snippet below the page title in search results.
It serves as a preview of the page’s content and can greatly influence whether users decide to click on the link or not. A well-crafted and compelling meta description can attract more clicks and improve your click-through rate (CTR). - User Engagement: A well-written meta description provides a concise and relevant description of the page’s content. It helps users understand what the page is about and whether it aligns with their needs or interests. By accurately representing the content, it can attract the right audience and increase user engagement on your website.
- Social Media Sharing: When a web page is shared on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, or LinkedIn, the meta description often gets pulled as the default description. It influences how the shared post appears and can impact engagement and click-through rates on social media.
- Context for Search Engines: While meta descriptions don’t directly affect search engine rankings, they provide context to search engine algorithms about the content of the page. Search engines may consider the keywords and phrases in the meta description when determining the relevance of a page to a search query.
How to write a meta description?
When writing a meta description for a web page, it is important to keep the following best practices in mind:
- Keep it short: Try to keep your meta description between 50 and 160 characters. This will ensure that your entire description is displayed in search engine results.
- Be informative: Your meta description should accurately describe the content of the page. Use clear, descriptive language that will help potential visitors understand what they can expect to find on the page.
- Use keywords: Include relevant keywords in your meta description.
- Avoid duplication: Use the meta description to provide additional context or information about the page.
- Consider a call-to-action: Consider including a call-to-action in your meta description. This can help entice potential visitors to click through to your site.
- Use proper grammar and punctuation: Make sure that your meta description is well-written, free of spelling errors, and uses proper grammar and punctuation.
- To write a meta tag for a web page, create a concise and descriptive sentence that accurately summarizes the content of the page, including relevant keywords and key information to entice users and improve search engine visibility.
- When crafting a meta tag for a web blog, condense the main focus of the blog post into a concise and engaging sentence that includes relevant keywords, entices readers, and enhances search engine optimization.
How do title and description tags help in SEO?
Title and description tags are important on-page optimization elements that can significantly impact SEO.
Some of the ways they help SEO are as follows:
- Improved visibility in search results: The page title and description tags are the first thing that users see when your site appears in search results. A well-written and relevant title tag can help improve click-through rates, improving your site’s overall visibility in search results.
- Increased keyword relevance: Including relevant keywords in your page title and description tags can help search engines understand what your page is about.
- Improved user experience: A clear and concise page title and description can help users quickly understand what your page is about and whether it is relevant to their needs. This can improve the user experience and reduce bounce rates.
- Better indexing: Search engines use page titles and description tags to understand your site’s content. This can improve the likelihood that your site will be indexed properly and that all your pages will be included in search results.
What is a Canonical Tag ?
The canonical tag, often referred to as the rel=”canonical” tag, is an HTML element used in web development to address issues related to duplicate content.
It helps website owners and developers indicate the preferred version of a web page when multiple versions with similar content exist.
This tag is particularly valuable for search engine optimization (SEO) purposes.
When search engines crawl the web, they may encounter identical or very similar content across different URLs.
This can happen due to various reasons, such as tracking parameters, URL variations, or content management system (CMS) configurations. The canonical tag provides a way to inform search engines about the primary or preferred version of a page (Learn more about the beginners guide for canonical tag)
The syntax of the canonical tag looks like this:
html
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/preferred-url” />
Here, the href attribute contains the URL of the preferred version of the page.
By including this tag in the HTML head section of a page, website owners guide search engines to index and rank the specified URL as the primary one, consolidating the SEO value and avoiding the negative impact of duplicate content.
In summary, the canonical tag is a tool used to manage duplicate content issues and improve the accuracy of search engine results, ultimately contributing to a better user experience and more effective SEO strategies.
What is An Alt Text Tag?
The Alt Text (alternative text) tag is an HTML attribute used to provide a text description for images on a web page.
It serves as an alternative when the image cannot be displayed or when a user is utilizing a screen reader.
Alt text is a crucial element for web accessibility, ensuring that individuals with visual impairments can understand and interpret the content of images. (Learn more on how Alt text tags can help you.)
The syntax for the Alt Text tag is as follows:
html
<img src=”image.jpg” alt=”Description of the image”>
In this example, the alt attribute contains the descriptive text for the image.
It should convey the essential information or context of the image, allowing users with visual disabilities to comprehend its meaning.
Alt text is beneficial for several reasons:
- Accessibility: Alt text makes web content more accessible to people with visual impairments, as screen readers can read aloud the description of images.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Search engines use alt text to understand the content of images, contributing to the overall SEO of a webpage.
- User Experience: When images fail to load, users will see the alt text, providing context about the missing image.
To create effective alt text, it’s important to be concise and descriptive, conveying the core information of the image without unnecessary details.
Additionally, decorative images that don’t convey meaningful content can have empty or null alt text (alt=””).
This indicates to assistive technologies that the image is decorative and doesn’t require a description.
What is a Viewport Meta Tag ?
The viewport meta tag is a crucial element in web development that helps control the layout and behavior of a webpage on different devices.
It is particularly important for responsive web design, which aims to provide an optimal viewing experience across various screen sizes and resolutions.
The viewport meta tag is typically added to the head section of an HTML document and includes the following attributes:
- Width: The width attribute sets the width of the viewport to a specific value or to the device’s width.
- Initial-scale: The initial-scale attribute specifies the initial zoom level when the webpage is loaded. It can be set to a value between 0.1 and 10, with 1 being the default value. A value of “1.0” ensures that the webpage is displayed at a 1:1 ratio to the device’s screen.
- User-scalable: The user-scalable attribute determines whether users can zoom in or out of the webpage. Setting it to “yes” allows users to zoom, while setting it to “no” disables zooming.
The viewport meta tag enables web developers to adapt the layout, text, and graphics of a webpage to fit different devices, ensuring an optimal viewing experience for users.
What is Meta Robots Tag ?
The meta robots tag is an HTML meta tag that provides instructions to search engine crawlers about how they should handle indexing and following links on a webpage.
It helps control the visibility and accessibility of web pages in search engine results.
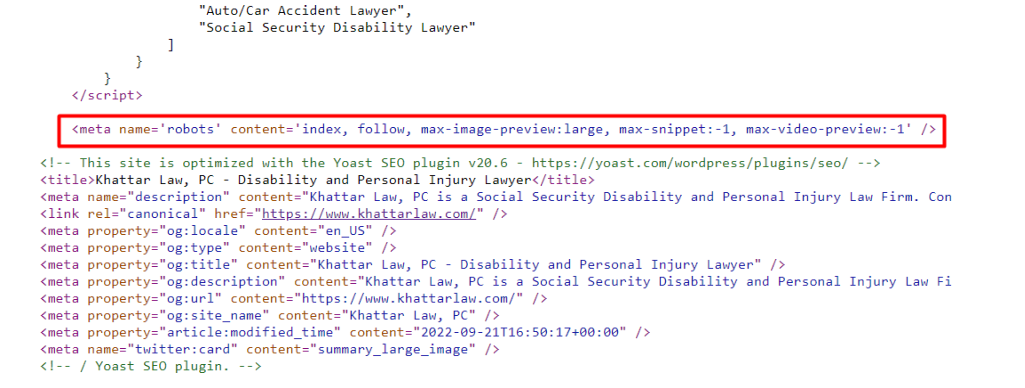
The meta robots tag is typically placed in the head section of an HTML document and includes various directives.
Some of the commonly used directives with the meta robots tag:
- “index”: This directive tells search engine crawlers to include the webpage in search results. It is the default behavior if no meta robots tag is specified.
- “noindex”: When this directive is used, search engines are instructed not to include the webpage in their search results. It can be useful for pages that are under construction, have duplicate content, or should not be indexed for other reasons.
- “follow”: With this directive, search engine crawlers are instructed to follow and crawl the links present on the webpage. It is the default behavior if no meta robots tag is specified.
- “nofollow”: This directive tells search engine crawlers not to follow the links on the webpage. It is commonly used to prevent the crawling of specific links, such as user-generated content or sponsored links.
Open Graph (OG) Tag
The Open Graph (OG) tag is an HTML meta tag used to control how a web page appears when shared on social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and others. It allows you to customize the title, description, image, and other elements displayed in the social media preview when a web page is shared.
- Customization: The Open Graph protocol enables you to provide specific information about your webpage to social media platforms. By including Open Graph tags, you can control how the shared content is presented, making it more engaging and enticing for users.
- Elements: The Open Graph tag includes several important elements:
- og:title: Specifies the title of the shared content.
- og:description: Provides a brief description of the content.
- og:image: Specifies the image that represents the shared content.
- og:url: Indicates the canonical URL of the shared content.
- og:type: Specifies the type of content (e.g., article, website, video, etc.).
- Implementation: To use the Open Graph tag, add the appropriate meta tags to the head section of your HTML document.
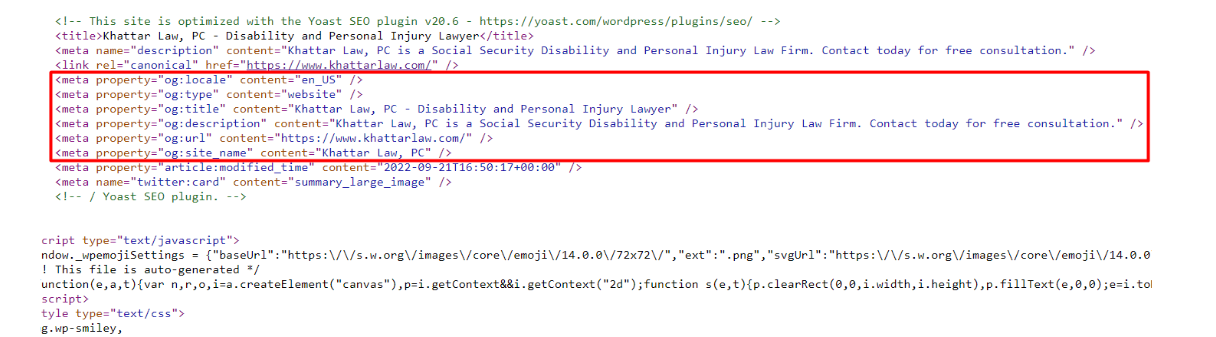
- Social Media Preview: When a web page is shared on social media, platforms retrieve the Open Graph tags to display a preview of the shared content. This preview typically includes the title, description, and image specified in the Open Graph tags.
- Benefits: By optimizing your Open Graph tags, you can enhance the visual appeal and relevance of your shared content.
This can increase click-through rates, drive more traffic to your webpage, and improve overall user engagement on social media platforms.
What is Header Tag ?
A header or an HTML heading tag defines headings and subheadings within a webpage.
Header tags range from <h1> to <h6>, where <h1> represents the main heading and <h6> represents the smallest subheading.
These tags not only help organize content hierarchically but also play a significant role in search engine optimization (SEO) by indicating the importance of different sections on a webpage. Proper use of header tags improves a website’s structure, readability, and SEO.
Do meta tags help in SEO?
Yes, meta tags can help with search engine optimization (SEO) by providing information and signals to search engines about the content and relevance of a webpage.
While meta tags alone may not directly impact search engine rankings, they play a significant role in improving the visibility and click-through rates of web pages in search engine results.
Critical Takeaways for the Role of Meta Tags
In the realm of on-page optimization, meta tags serve as integral signposts that guide search engines and enhance a website’s visibility.
The title tag is a pivotal player, demanding a delicate balance between being captivating, concise, and rich in keywords to secure a prime spot on search engine results pages.
Caution prevails against keyword stuffing, emphasizing the importance of a natural integration that prioritizes relevance. Canonical tags step in as problem solvers, addressing duplicate content concerns and steering search engines toward preferred versions of pages.
FAQs on Meta Tags
1. How do I find meta tags on a website?
To find meta tags on a website, you can view the page source by right-clicking on the web page and selecting “View Page Source” or “Inspect.” This will display the HTML source code of the webpage.
Within the source code, you can search for meta tags by using the browser’s search function (Ctrl+F or Command+F) and looking for lines that start with “<meta” and contain attributes such as “name” or “property.”
These attributes provide information about the type and purpose of the meta tags, allowing you to examine and analyze them for SEO optimization or other purposes.
2. How do I add meta tags to my URL?
To add meta tags to your URL, you need to edit the HTML code of your webpage. Locate the <head> section within the HTML file and add meta tags using the <meta> HTML element. For example, you can include a meta title tag (<title>) to define the title of your page, a meta description tag (<meta name=”description” content=”…”>) to provide a brief summary of the page content, and a meta keywords tag (<meta name=”keywords” content=”…”>) to specify relevant keywords.
Ensure the meta tags accurately reflect the content of your page and optimize them for search engine visibility. Once the meta tags are added, save the HTML file and upload it to your website to apply the changes.
3. Is it necessary to have a title tag?
Yes, it is necessary to have a title tag for each web page. The title tag is an essential element of HTML and plays a crucial role in both search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience.
Search engines use the title tag to understand the topic and relevance of a webpage, and it is typically displayed as the clickable headline in search engine results. Users rely on the title tag to quickly identify the content of a page and determine its relevance to their search query.
4. Do websites still use meta tags?
Yes, websites still use meta tags. While the importance of meta tags for SEO has evolved over time, they continue to serve various purposes and are widely implemented on websites. While search engines may not rely heavily on meta tags alone for ranking purposes, they still use them to gather information about the webpage’s content.
Moreover, meta tags like the meta title and meta description tags often appear in search engine results, influencing click-through rates and providing users with a preview of the page’s content.
5. Why do title tags matter?
Title tags are an important aspect of on-page optimization for search engine optimization (SEO). Title tags are displayed prominently in search engine results as the clickable headline for each search result.
As a result, the page title for a website is the first impression potential visitors will have of your website, and it can significantly impact whether or not they choose to click through to your site.
Recent Post
Contact Us
